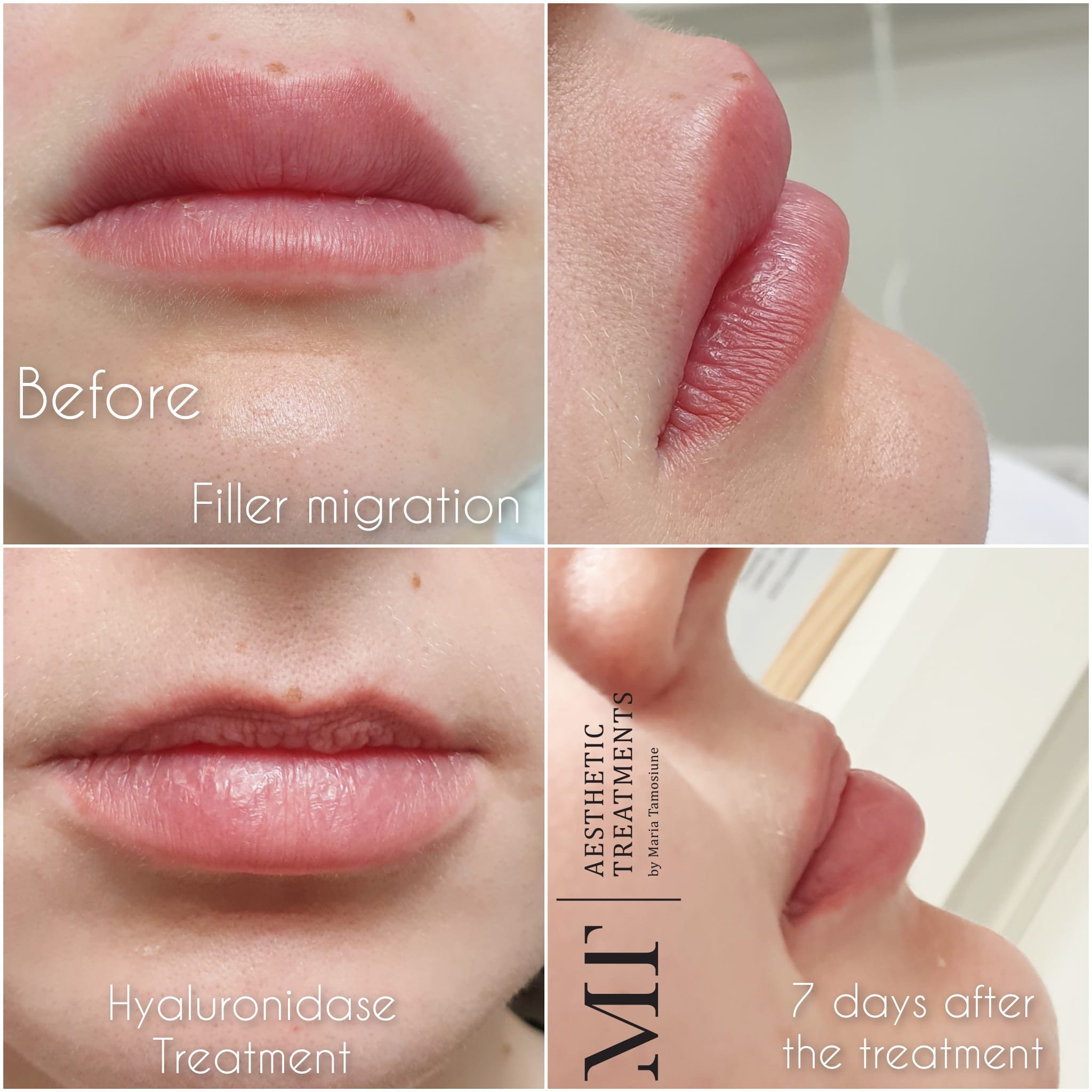
HA FILLER DISSOLVING, HYALURONIDASE
-
Hyaluronic acid responds to hyaluronidase through a mechanism of breaking the glucosaminidic bond of the HA product and stimulating tissue absorption in the area. The destruction of this bond changes the molecular structure, or the moiety, of the product's cohesiveness. It thus allows the product to be infiltrated by the body's own process for absorption of the residual by-products due to the dispersion. The amount of product hydrolysis is directly related to the quantity of hyaluronidase that is injected, and the full resolution of the impact of hyaluronidase occurs relatively quickly. It should be fully resolved by 48 hours post-treatment.
HYALURONIDASE
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme used in cosmetic procedures to dissolve hyaluronic acid-based fillers. While it plays a valuable role in correcting filler-related complications and achieving desired outcomes, practitioners and clients must be aware of its contraindications, potential side effects, and interactions with other drugs.
BACKGROUND
Hyaluronidase is found in humans and multiple sources of animals, including various venoms, ovine or bovine testes, and human serum.
The substance has been widely utilised throughout medicine because of its ability to increase the degradation of the extracellular matrix of HA and the tissue's permeability.
The most common source of hyaluronidase remains ovine and bovine, and a recombinant DNA methodology produces it. The recombinant DNA is purified glycoproteins formed by using amino acids that are then placed in a sterile, nonpreserved solution. As with any industry, variances are common in producing compounded hyaluronidase. It may be processed differently based on its various indications, such as cosmetic, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical or injectable grade hyaluronidase.
Hyaluronidase is the substance recommended for the treatment of adverse events with HA fillers.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Hyaluronic acid responds to hyaluronidase through a mechanism of breaking the glucosaminidic bond of the HA product and stimulating tissue absorption in the area. The destruction of this bond changes the molecular structure, or the moiety, of the product's cohesiveness. It thus allows the product to be infiltrated by the body's own process for absorption of the residual by-products due to the dispersion. The amount of product hydrolysis is directly related to the quantity of hyaluronidase that is injected, and the full resolution of the impact of hyaluronidase occurs relatively quickly. It should be fully resolved by 48 hours post-treatment.
!CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Allergies or Sensitivities: Individuals with known allergies or hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase or any of its components should avoid its use.
· PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
· ACTIVE INFECTIONS OR INFLAMMATORY SKIN CONDITIONS
· AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS
!SIDE EFFECTS:
LOCAL REACTIONS: Common side effects include redness, swelling, bruising, and tenderness at the injection site. These effects are typically mild and temporary.
ALLERGIC REACTIONS: While rare, allergic reactions can occur. Signs may include itching, rash, hives, or swelling. Immediate medical attention is necessary if an allergic reaction is suspected.
PAIN AND DISCOMFORT: Some clients may experience discomfort or pain at the injection site, which usually subsides within a few days.
TOPICAL MEDICATIONS: The concurrent use of topical medications or skin care products in the treated area should be discussed with the practitioner, as interactions could affect treatment outcomes.
BLOOD THINNERS: Clients taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, may experience increased bruising or bleeding at the injection site. Adjustments to medication regimens may be necessary before the procedure.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDICATIONS AND OTHER DRUGS: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can increase the risk of bleeding or bruising, potentially affecting recovery after hyaluronidase injections. Drugs which can cause possible reactions with hyaluronidase:
- Phenytoin
- Furosemide
- Dopamine
- Benzodiazepine
- Alpha-adrenergic agonists (ibuprofen, aspirin, diclofenac, antihistamines)
In case of any doubts, refer to BNF, prescriber or pharmacist.
HERBAL SUPPLEMENTS: Herbal supplements that affect blood clotting, such as ginkgo biloba, garlic, or ginger, may interact with hyaluronidase treatment. Clients should disclose all supplements they are taking.
ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK: A severe allergic reaction found in 1-2 in 1000 people.
THE TREATMENT INCLUDES:
· COMPREHENSIVE CONSULTATION
· INFORMED CONSENT
· INDIVIDUALIZED APPROACH
The only true contraindication for using hyaluronidase is in patients with known sensitivity to the medication or any of its stabilising components, which may be present due to the product's compounding. An allergic reaction to hyaluronidase is uncommon, and currently, prior skin testing is considered unnecessary because of the low incidence rate of adverse reactions (0.1% urticarial or angioedema). However, if the recipient has a history of significant allergies, it may be warranted to perform a skin test, given the severity of potential HA adverse events. The skin test would involve placing a small bolus of subcutaneous injection of 0.02 ml (three units of 150 units/ml) under the skin surface, which would be monitored. It would be considered positive if a reaction appeared after 5 minutes of observation to a maximum of 30 minutes after a patch test was done.
DISSOLVING SHOULD BE CONSIDERED IN THESE CASES (NON-EMERGENCY CASE)
1. OVERFILLING OR UNEVEN RESULTS
2. CHANGE IN AESTHETIC PREFERENCES
3. ADDRESSING COMPLICATIONS
4. DISCOMFORT OR SENSATION CHANGES
5. LIFESTYLE CHANGES
6. ALLERGIC REACTIONS OR SENSITIVITIES
7. CUSTOMIZED DISSOLVING